AI เจนเนอเรชั่นคืออะไรและทำงานอย่างไร
เผยแพร่แล้ว: 2023-09-26Generative AI ซึ่งเป็นส่วนย่อยของปัญญาประดิษฐ์ ได้กลายเป็นพลังปฏิวัติในโลกเทคโนโลยี แต่มันคืออะไรกันแน่? และเหตุใดจึงได้รับความสนใจมาก?
คู่มือเชิงลึกนี้จะเจาะลึกเกี่ยวกับวิธีการทำงานของโมเดล AI ทั่วไป สิ่งที่ทำได้และทำไม่ได้ และผลกระทบขององค์ประกอบทั้งหมดเหล่านี้
AI เจนเนอเรชั่นคืออะไร?
Generative AI หรือ genAI หมายถึงระบบที่สามารถสร้างเนื้อหาใหม่ได้ ไม่ว่าจะเป็นข้อความ รูปภาพ เพลง หรือแม้แต่วิดีโอ ตามเนื้อผ้า AI/ML หมายถึงสามสิ่ง: การเรียนรู้แบบมีผู้ดูแล ไม่ได้รับการดูแล และการเรียนรู้แบบเสริมกำลัง แต่ละรายการให้ข้อมูลเชิงลึกตามผลลัพธ์ของการจัดกลุ่ม
โมเดล AI แบบไม่สร้างสรรค์ทำการคำนวณตามอินพุต (เช่น การจัดหมวดหมู่รูปภาพหรือการแปลประโยค) ในทางตรงกันข้าม แบบจำลองกำเนิดจะสร้างผลลัพธ์ "ใหม่" เช่น การเขียนเรียงความ การแต่งเพลง การออกแบบกราฟิก และแม้กระทั่งการสร้างใบหน้ามนุษย์ที่สมจริงซึ่งไม่มีอยู่ในโลกแห่งความเป็นจริง
ผลกระทบของเจเนอเรชั่นเอไอ
การเพิ่มขึ้นของ generative AI มีผลกระทบที่สำคัญ ด้วยความสามารถในการสร้างเนื้อหา อุตสาหกรรมต่างๆ เช่น บันเทิง การออกแบบ และสื่อสารมวลชน กำลังเผชิญกับการเปลี่ยนแปลงกระบวนทัศน์
ตัวอย่างเช่น สำนักข่าวสามารถใช้ AI เพื่อร่างรายงาน ในขณะที่นักออกแบบสามารถรับคำแนะนำเกี่ยวกับกราฟิกที่ได้รับความช่วยเหลือจาก AI AI สามารถสร้างสโลแกนโฆษณาได้หลายร้อยรายการในไม่กี่วินาที ไม่ว่าตัวเลือกเหล่านั้นจะดีหรือไม่ก็ตาม หรือไม่ก็เป็นอีกเรื่องหนึ่ง
Generative AI สามารถสร้างเนื้อหาที่ปรับแต่งให้เหมาะกับผู้ใช้แต่ละราย ลองนึกถึงแอปเพลงที่แต่งเพลงไม่ซ้ำใครตามอารมณ์ของคุณ หรือแอปข่าวที่ร่างบทความเกี่ยวกับหัวข้อที่คุณสนใจ
ปัญหาก็คือ เนื่องจาก AI มีบทบาทสำคัญในการสร้างเนื้อหา คำถามเกี่ยวกับความถูกต้อง ลิขสิทธิ์ และคุณค่าของความคิดสร้างสรรค์ของมนุษย์จึงแพร่หลายมากขึ้น
generative AI ทำงานอย่างไร
หัวใจสำคัญของ Generative AI คือการคาดการณ์ข้อมูลส่วนถัดไปในลำดับ ไม่ว่าจะเป็นคำถัดไปในประโยคหรือพิกเซลถัดไปในรูปภาพ เรามาดูรายละเอียดว่าสิ่งนี้เกิดขึ้นได้อย่างไร
แบบจำลองทางสถิติ
แบบจำลองทางสถิติเป็นหัวใจสำคัญของระบบ AI ส่วนใหญ่ พวกเขาใช้สมการทางคณิตศาสตร์เพื่อแสดงความสัมพันธ์ระหว่างตัวแปรต่างๆ
สำหรับ AI เชิงสร้างสรรค์ โมเดลจะได้รับการฝึกให้จดจำรูปแบบในข้อมูล จากนั้นจึงใช้รูปแบบเหล่านี้เพื่อสร้าง ข้อมูลใหม่ที่คล้ายกัน
หากแบบจำลองได้รับการฝึกฝนเกี่ยวกับประโยคภาษาอังกฤษ โมเดลจะเรียนรู้ความน่าจะเป็นทางสถิติของคำหนึ่งคำต่อจากอีกคำหนึ่ง ซึ่งช่วยให้สามารถสร้างประโยคที่สอดคล้องกันได้
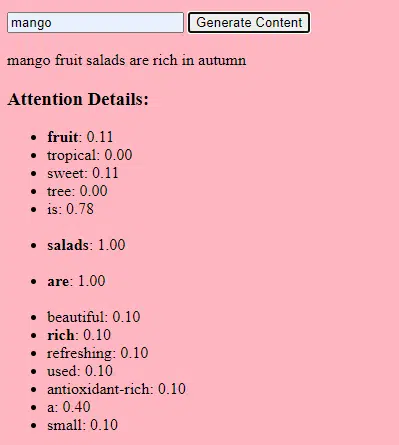
การรวบรวมข้อมูล
ทั้งคุณภาพและปริมาณของข้อมูลมีความสำคัญ โมเดลเจนเนอเรทีฟได้รับการฝึกฝนบนชุดข้อมูลขนาดใหญ่เพื่อทำความเข้าใจรูปแบบ
สำหรับโมเดลภาษา อาจหมายถึงการนำเข้าคำศัพท์หลายพันล้านคำจากหนังสือ เว็บไซต์ และข้อความอื่นๆ
สำหรับโมเดลรูปภาพ อาจหมายถึงการวิเคราะห์รูปภาพหลายล้านรูป ยิ่งข้อมูลการฝึกอบรมมีความหลากหลายและครอบคลุมมากเท่าใด โมเดลก็จะยิ่งสร้างผลลัพธ์ที่หลากหลายได้ดีขึ้นเท่านั้น
หม้อแปลงไฟฟ้าและความสนใจทำงานอย่างไร
หม้อแปลงไฟฟ้าเป็นสถาปัตยกรรมโครงข่ายประสาทเทียมประเภทหนึ่งที่นำมาใช้ในรายงานปี 2017 เรื่อง “Attention Is All You Need” โดย Vaswani และคณะ นับตั้งแต่นั้นมาสิ่งเหล่านี้ได้กลายเป็นรากฐานสำหรับโมเดลภาษาที่ล้ำสมัยส่วนใหญ่ ChatGPT จะไม่ทำงานหากไม่มีหม้อแปลง
กลไก "ความสนใจ" ช่วยให้โมเดลสามารถมุ่งเน้นไปที่ส่วนต่างๆ ของข้อมูลอินพุต เช่นเดียวกับการที่มนุษย์ให้ความสนใจกับคำเฉพาะเมื่อทำความเข้าใจประโยค
กลไกนี้ช่วยให้โมเดลตัดสินใจว่าส่วนใดของอินพุตที่เกี่ยวข้องกับงานที่กำหนด ทำให้มีความยืดหยุ่นและทรงพลังสูง
รหัสด้านล่างเป็นรายละเอียดพื้นฐานของกลไกของหม้อแปลงไฟฟ้า โดยอธิบายแต่ละชิ้นเป็นภาษาอังกฤษธรรมดา
class Transformer: # Convert words to vectors # What this is : turns words into "vector embeddings" –basically numbers that represent the words and their relationships to each other. # Demo : "the pineapple is cool and tasty" -> [0.2, 0.5, 0.3, 0.8, 0.1, 0.9] self.embedding = Embedding(vocab_size, d_model) # Add position information to the vectors # What this is : Since words in a sentence have a specific order, we add information about each word's position in the sentence. # Demo : "the pineapple is cool and tasty" with position -> [0.2+0.01, 0.5+0.02, 0.3+0.03, 0.8+0.04, 0.1+0.05, 0.9+0.06] self.positional_encoding = PositionalEncoding(d_model) # Stack of transformer layers # What this is : Multiple layers of the Transformer model stacked on top of each other to process data in depth. # Why it does it : Each layer captures different patterns and relationships in the data. # Explained like I'm five : Imagine a multi-story building. Each floor (or layer) has people (or mechanisms) doing specific jobs. The more floors, the more jobs get done! self.transformer_layers = [TransformerLayer(d_model, nhead) for _ in range(num_layers)] # Convert the output vectors to word probabilities # What this is : A way to predict the next word in a sequence. # Why it does it : After processing the input, we want to guess what word comes next. # Explained like I'm five : After listening to a story, this tries to guess what happens next. self.output_layer = Linear(d_model, vocab_size) def forward(self, x): # Convert words to vectors, as above x = self.embedding(x) # Add position information, as above x = self.positional_encoding(x) # Pass through each transformer layer # What this is : Sending our data through each floor of our multi-story building. # Why it does it : To deeply process and understand the data. # Explained like I'm five : It's like passing a note in class. Each person (or layer) adds something to the note before passing it on, which can end up with a coherent story – or a mess. for layer in self.transformer_layers: x = layer(x) # Get the output word probabilities # What this is : Our best guess for the next word in the sequence. return self.output_layer(x)ในโค้ด คุณอาจมีคลาส Transformer และคลาส TransformerLayer คลาสเดียว นี่เหมือนกับการมีพิมพ์เขียวสำหรับพื้นเทียบกับทั้งอาคาร
โค้ด TransformerLayer นี้จะแสดงให้คุณเห็นว่าส่วนประกอบเฉพาะ เช่น ความสนใจแบบหลายหัวและการจัดเตรียมเฉพาะทำงานอย่างไร
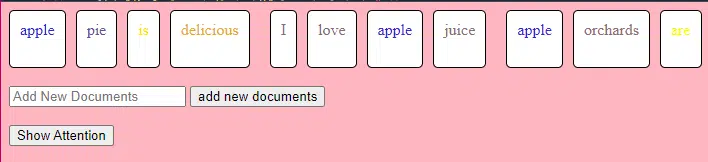
class TransformerLayer: # Multi-head attention mechanism # What this is : A mechanism that lets the model focus on different parts of the input data simultaneously. # Demo : "the pineapple is cool and tasty" might become "this PINEAPPLE is COOL and TASTY" as the model pays more attention to certain words. self.attention = MultiHeadAttention(d_model, nhead) # Simple feed-forward neural network # What this is : A basic neural network that processes the data after the attention mechanism. # Demo : "this PINEAPPLE is COOL and TASTY" -> [0.25, 0.55, 0.35, 0.85, 0.15, 0.95] (slight changes in numbers after processing) self.feed_forward = FeedForward(d_model) def forward(self, x): # Apply attention mechanism # What this is : The step where we focus on different parts of the sentence. # Explained like I'm five : It's like highlighting important parts of a book. attention_output = self.attention(x, x, x) # Pass the output through the feed-forward network # What this is : The step where we process the highlighted information. return self.feed_forward(attention_output)โครงข่ายประสาทเทียมแบบป้อนไปข้างหน้าเป็นหนึ่งในโครงข่ายประสาทเทียมที่ง่ายที่สุด ประกอบด้วยเลเยอร์อินพุต หนึ่งเลเยอร์ที่ซ่อนอยู่ และเลเยอร์เอาท์พุต
ข้อมูลไหลไปในทิศทางเดียว - จากเลเยอร์อินพุต ผ่านเลเยอร์ที่ซ่อนอยู่ และไปยังเลเยอร์เอาต์พุต ไม่มีการวนซ้ำหรือวนซ้ำในเครือข่าย
ในบริบทของสถาปัตยกรรมหม้อแปลงไฟฟ้า โครงข่ายประสาทเทียมแบบฟีดไปข้างหน้าจะใช้หลังจากกลไกความสนใจในแต่ละเลเยอร์ เป็นการแปลงเชิงเส้นสองชั้นอย่างง่ายโดยมีการเปิดใช้งาน ReLU อยู่ระหว่างนั้น
# Scaled dot-product attention mechanism class ScaledDotProductAttention: def __init__(self, d_model): # Scaling factor helps in stabilizing the gradients # it reduces the variance of the dot product. # What this is: A scaling factor based on the size of our model's embeddings. # What it does : Helps to make sure the dot products don't get too big. # Why it does it : Big dot products can make a model unstable and harder to train. # How it does it : By dividing the dot products by the square root of the embedding size. # It's used when calculating attention scores. # Explained like I'm five : Imagine you shouted something really loud. This scaling factor is like turning the volume down so it's not too loud. self.scaling_factor = d_model ** 0.5 def forward(self, query, key, value): # What this is : The function that calculates how much attention each word should get. # What it does : Determines how relevant each word in a sentence is to every other word. # Why it does it : So we can focus more on important words when trying to understand a sentence. # How it does it : By taking the dot product (the numeric product: a way to measure similarity) of the query and key, then scaling it, and finally using that to weigh our values. # How it fits into the rest of the code : This function is called whenever we want to calculate attention in our model. # Explained like I'm five : Imagine you have a toy and you want to see which of your friends likes it the most. This function is like asking each friend how much they like the toy, and then deciding who gets to play with it based on their answers. # Calculate attention scores by taking the dot product of the query and key. scores = dot_product(query, key) / self.scaling_factor # Convert the raw scores to probabilities using the softmax function. attention_weights = softmax(scores) # Weight the values using the attention probabilities. return dot_product(attention_weights, value) # Feed-forward neural network # This is an extremely basic example of a neural network. class FeedForward: def __init__(self, d_model): # First linear layer increases the dimensionality of the data. self.layer1 = Linear(d_model, d_model * 4) # Second linear layer brings the dimensionality back to d_model. self.layer2 = Linear(d_model * 4, d_model) def forward(self, x): # Pass the input through the first layer, #Pass the input through the first layer: # Input : This refers to the data you feed into the neural network. I # First layer : Neural networks consist of layers, and each layer has neurons. When we say "pass the input through the first layer," we mean that the input data is being processed by the neurons in this layer. Each neuron takes the input, multiplies it by its weights (which are learned during training), and produces an output. # apply ReLU activation to introduce non-linearity, # and then pass through the second layer. #ReLU activation: ReLU stands for Rectified Linear Unit. # It's a type of activation function, which is a mathematical function applied to the output of each neuron. In simpler terms, if the input is positive, it returns the input value; if the input is negative or zero, it returns zero. # Neural networks can model complex relationships in data by introducing non-linearities. # Without non-linear activation functions, no matter how many layers you stack in a neural network, it would behave just like a single-layer perceptron because summing these layers would give you another linear model. # Non-linearities allow the network to capture complex patterns and make better predictions. return self.layer2(relu(self.layer1(x))) # Positional encoding adds information about the position of each word in the sequence. class PositionalEncoding: def __init__(self, d_model): # What this is : A setup to add information about where each word is in a sentence. # What it does : Prepares to add a unique "position" value to each word. # Why it does it : Words in a sentence have an order, and this helps the model remember that order. # How it does it : By creating a special pattern of numbers for each position in a sentence. # How it fits into the rest of the code : Before processing words, we add their position info. # Explained like I'm five : Imagine you're in a line with your friends. This gives everyone a number to remember their place in line. pass def forward(self, x): # What this is : The main function that adds position info to our words. # What it does : Combines the word's original value with its position value. # Why it does it : So the model knows the order of words in a sentence. # How it does it : By adding the position values we prepared earlier to the word values. # How it fits into the rest of the code : This function is called whenever we want to add position info to our words. # Explained like I'm five : It's like giving each of your toys a tag that says if it's the 1st, 2nd, 3rd toy, and so on. return x # Helper functions def dot_product(a, b): # Calculate the dot product of two matrices. # What this is : A mathematical operation to see how similar two lists of numbers are. # What it does : Multiplies matching items in the lists and then adds them up. # Why it does it : To measure similarity or relevance between two sets of data. # How it does it : By multiplying and summing up. # How it fits into the rest of the code : Used in attention to see how relevant words are to each other. # Explained like I'm five : Imagine you and your friend have bags of candies. You both pour them out and match each candy type. Then, you count how many matching pairs you have. return a @ b.transpose(-2, -1) def softmax(x): # Convert raw scores to probabilities ensuring they sum up to 1. # What this is : A way to turn any list of numbers into probabilities. # What it does : Makes the numbers between 0 and 1 and ensures they all add up to 1. # Why it does it : So we can understand the numbers as chances or probabilities. # How it does it : By using exponentiation and division. # How it fits into the rest of the code : Used to convert attention scores into probabilities. # Explained like I'm five : Lets go back to our toys. This makes sure that when you share them, everyone gets a fair share, and no toy is left behind. return exp(x) / sum(exp(x), axis=-1) def relu(x): # Activation function that introduces non-linearity. It sets negative values to 0. # What this is : A simple rule for numbers. # What it does : If a number is negative, it changes it to zero. Otherwise, it leaves it as it is. # Why it does it : To introduce some simplicity and non-linearity in our model's calculations. # How it does it : By checking each number and setting it to zero if it's negative. # How it fits into the rest of the code : Used in neural networks to make them more powerful and flexible. # Explained like I'm five : Imagine you have some stickers, some are shiny (positive numbers) and some are dull (negative numbers). This rule says to replace all dull stickers with blank ones. return max(0, x)AI แบบสร้างสรรค์ทำงานอย่างไร – พูดง่ายๆ ก็คือ
คิดว่า AI กำเนิดเป็นการทอยลูกเต๋าถ่วงน้ำหนัก ข้อมูลการฝึกอบรมจะกำหนดน้ำหนัก (หรือความน่าจะเป็น)
หากลูกเต๋าแทนคำถัดไปในประโยค คำที่มักจะตามหลังคำปัจจุบันในข้อมูลการฝึกจะมีน้ำหนักมากกว่า ดังนั้น "ท้องฟ้า" อาจตามหลัง "สีน้ำเงิน" บ่อยกว่า "กล้วย" เมื่อ AI “ทอยลูกเต๋า” เพื่อสร้างเนื้อหา ก็มีแนวโน้มที่จะเลือกลำดับที่เป็นไปได้ทางสถิติมากขึ้นตามการฝึกฝน
แล้ว LLM สามารถสร้างเนื้อหาที่ “ดูเหมือน” เป็นต้นฉบับได้อย่างไร?
มาดูรายการปลอม – “ของขวัญ Eid al-Fitr ที่ดีที่สุดสำหรับนักการตลาดเนื้อหา” – และอธิบายว่า LLM สามารถสร้างได้อย่างไร รายการนี้โดยรวมข้อความจากเอกสารเกี่ยวกับของขวัญ วันอีด และนักการตลาดเนื้อหา
ก่อนการประมวลผล ข้อความจะถูกแบ่งออกเป็นส่วนเล็กๆ ที่เรียกว่า "โทเค็น" โทเค็นเหล่านี้อาจสั้นเท่ากับหนึ่งอักขระหรือยาวเท่ากับหนึ่งคำ
ตัวอย่าง: “Eid al-Fitr คือการเฉลิมฉลอง” กลายเป็น [“Eid”, “al-Fitr”, “คือ”, “a”, “การเฉลิมฉลอง”]
ซึ่งช่วยให้โมเดลทำงานกับข้อความจำนวนมากที่สามารถจัดการได้และเข้าใจโครงสร้างของประโยค
จากนั้นแต่ละโทเค็นจะถูกแปลงเป็นเวกเตอร์ (รายการตัวเลข) โดยใช้การฝัง เวกเตอร์เหล่านี้จับความหมายและบริบทของแต่ละคำ
การเข้ารหัสตำแหน่งจะเพิ่มข้อมูลให้กับเวกเตอร์แต่ละคำเกี่ยวกับตำแหน่งในประโยค เพื่อให้แน่ใจว่าโมเดลจะไม่สูญเสียข้อมูลลำดับนี้
จากนั้น เราใช้ กลไกความสนใจ : สิ่งนี้ทำให้โมเดลสามารถโฟกัสไปที่ส่วนต่างๆ ของข้อความอินพุตเมื่อสร้างเอาต์พุต หากคุณจำ BERT ได้ นี่คือสิ่งที่น่าตื่นเต้นสำหรับชาว Googler เกี่ยวกับ BERT
หากแบบจำลองของเราได้เห็นข้อความเกี่ยวกับ " ของขวัญ " และรู้ว่าผู้คนให้ ของขวัญ ในระหว่าง การเฉลิมฉลอง และยังเห็นว่าข้อความเกี่ยวกับ " วันอีฎิ้ลฟิตริ " เป็นการ เฉลิมฉลอง ที่สำคัญ โมเดลก็จะให้ความสำคัญกับ " ความสนใจ " ต่อการเชื่อมโยงเหล่านี้
ในทำนองเดียวกัน หากเห็นข้อความเกี่ยวกับ “ นักการตลาดเนื้อหา ” ต้องการ เครื่องมือ หรือ ทรัพยากร เฉพาะ ก็สามารถเชื่อมโยงแนวคิดเรื่อง “ ของขวัญ ” กับ “ นักการตลาด เนื้อหา” ได้

ตอนนี้เราสามารถรวมบริบทได้: เมื่อโมเดลประมวลผลข้อความที่ป้อนผ่านเลเยอร์ Transformer หลายเลเยอร์ โมเดลจะรวมบริบทที่ได้เรียนรู้มา
ดังนั้น แม้ว่าข้อความต้นฉบับจะไม่เคยกล่าวถึง "ของขวัญ Eid al-Fitr สำหรับนักการตลาดเนื้อหา" แต่โมเดลก็สามารถรวบรวมแนวคิดของ "Eid al-Fitr" "ของขวัญ" และ "นักการตลาดเนื้อหา" เพื่อสร้างเนื้อหานี้ได้
เนื่องจากได้เรียนรู้บริบทที่กว้างขึ้นเกี่ยวกับคำศัพท์แต่ละคำเหล่านี้
หลังจากประมวลผลอินพุตผ่านกลไกความสนใจและเครือข่ายฟีดฟอร์เวิร์ดในแต่ละเลเยอร์ Transformer แล้ว โมเดลจะสร้างการกระจายความน่าจะเป็นเหนือคำศัพท์สำหรับคำถัดไปในลำดับ
อาจคิดว่าหลังจากคำว่า "ดีที่สุด" และ "Eid al-Fitr" คำว่า "ของขวัญ" มีความเป็นไปได้สูงที่จะเกิดขึ้นต่อไป ในทำนองเดียวกัน อาจเชื่อมโยง “ของขวัญ” กับผู้ที่อาจเป็นผู้รับ เช่น “นักการตลาดเนื้อหา”
รับจดหมายข่าวรายวันที่นักการตลาดวางใจ
ดูข้อกำหนด
แบบจำลองภาษาขนาดใหญ่ถูกสร้างขึ้นอย่างไร
การเดินทางจากโมเดลหม้อแปลงพื้นฐานไปจนถึงโมเดลภาษาขนาดใหญ่ที่ซับซ้อน (LLM) เช่น GPT-3 หรือ BERT เกี่ยวข้องกับการขยายขนาดและการปรับแต่งส่วนประกอบต่างๆ
ต่อไปนี้เป็นรายละเอียดทีละขั้นตอน:
LLM ได้รับการฝึกอบรมเกี่ยวกับข้อมูลข้อความจำนวนมหาศาล เป็นการยากที่จะอธิบายว่าข้อมูลนี้กว้างใหญ่เพียงใด
ชุดข้อมูล C4 ซึ่งเป็นจุดเริ่มต้นสำหรับ LLM จำนวนมากคือข้อมูลข้อความขนาด 750 GB นั่นคือ 805,306,368,000 ไบต์ ซึ่งเป็นข้อมูลจำนวนมาก ข้อมูลนี้อาจรวมถึงหนังสือ บทความ เว็บไซต์ กระดานสนทนา ส่วนความคิดเห็น และแหล่งที่มาอื่นๆ

ยิ่งข้อมูลมีความหลากหลายและครอบคลุมมากเท่าใด ความสามารถในการทำความเข้าใจและลักษณะทั่วไปของแบบจำลองก็จะยิ่งดีขึ้นเท่านั้น
แม้ว่าสถาปัตยกรรมหม้อแปลงพื้นฐานยังคงเป็นรากฐาน แต่ LLM ก็มีพารามิเตอร์จำนวนมากกว่ามาก ตัวอย่างเช่น GPT-3 มีพารามิเตอร์ 175 พันล้านพารามิเตอร์ ในกรณีนี้ พารามิเตอร์อ้างอิงถึงน้ำหนักและอคติในโครงข่ายประสาทเทียมที่เรียนรู้ในระหว่างกระบวนการฝึกอบรม
ในการเรียนรู้เชิงลึก โมเดลจะได้รับการฝึกให้คาดการณ์โดยการปรับพารามิเตอร์เหล่านี้เพื่อลดความแตกต่างระหว่างการคาดการณ์กับผลลัพธ์จริง
กระบวนการปรับพารามิเตอร์เหล่านี้เรียกว่าการปรับให้เหมาะสม ซึ่งใช้อัลกอริธึม เช่น การไล่ระดับลง
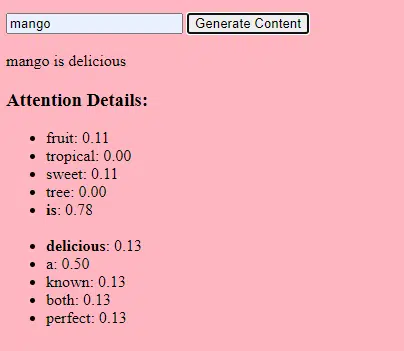
- น้ำหนัก: ค่าเหล่านี้เป็นค่าในโครงข่ายประสาทเทียมที่แปลงข้อมูลอินพุตภายในเลเยอร์ของเครือข่าย โดยจะมีการปรับเปลี่ยนระหว่างการฝึกเพื่อเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพเอาท์พุตของโมเดล การเชื่อมต่อระหว่างเซลล์ประสาทในชั้นที่อยู่ติดกันแต่ละครั้งจะมีน้ำหนักที่เกี่ยวข้องกัน
- อคติ: ค่าเหล่านี้ยังเป็นค่าในโครงข่ายประสาทเทียมที่ถูกเพิ่มเข้าไปในเอาต์พุตของการเปลี่ยนแปลงของเลเยอร์ โดยให้ระดับความอิสระเพิ่มเติมแก่โมเดล ช่วยให้พอดีกับข้อมูลการฝึกได้ดีขึ้น เซลล์ประสาทแต่ละอันในเลเยอร์มีความลำเอียงที่เกี่ยวข้องกัน
การปรับขนาดนี้ช่วยให้โมเดลจัดเก็บและประมวลผลรูปแบบและความสัมพันธ์ที่ซับซ้อนมากขึ้นในข้อมูลได้
พารามิเตอร์จำนวนมากยังหมายความว่าแบบจำลองต้องใช้พลังในการคำนวณและหน่วยความจำจำนวนมากสำหรับการฝึกอบรมและการอนุมาน นี่คือเหตุผลว่าทำไมการฝึกโมเดลดังกล่าวจึงต้องใช้ทรัพยากรมากและโดยทั่วไปจะใช้ฮาร์ดแวร์พิเศษ เช่น GPU หรือ TPU
แบบจำลองนี้ได้รับการฝึกฝนให้ทำนายคำถัดไปในลำดับโดยใช้ทรัพยากรการคำนวณอันทรงพลัง โดยจะปรับพารามิเตอร์ภายในตามข้อผิดพลาดที่เกิดขึ้น และปรับปรุงการคาดการณ์อย่างต่อเนื่อง
กลไกความสนใจเช่นเดียวกับที่เราได้พูดคุยกันถือเป็นหัวใจสำคัญของ LLM ช่วยให้โมเดลมุ่งเน้นไปที่ส่วนต่างๆ ของอินพุตเมื่อสร้างเอาต์พุต
ด้วยการชั่งน้ำหนักความสำคัญของคำต่างๆ ในบริบท กลไกความสนใจช่วยให้แบบจำลองสามารถสร้างข้อความที่สอดคล้องกันและเกี่ยวข้องกับบริบทได้ การดำเนินการในระดับมหึมานี้ช่วยให้ LLM ทำงานในแบบที่พวกเขาทำ
หม้อแปลงไฟฟ้าทำนายข้อความได้อย่างไร?
หม้อแปลงทำนายข้อความโดยการประมวลผลโทเค็นอินพุตผ่านหลายเลเยอร์ โดยแต่ละเลเยอร์มีกลไกความสนใจและเครือข่ายฟีดไปข้างหน้า
หลังจากประมวลผลแล้ว โมเดลจะสร้างการแจกแจงความน่าจะเป็นเหนือคำศัพท์สำหรับคำถัดไปในลำดับ โดยทั่วไปคำที่มีความน่าจะเป็นสูงสุดจะถูกเลือกเป็นการทำนาย
โมเดลภาษาขนาดใหญ่สร้างและฝึกฝนอย่างไร
การสร้าง LLM เกี่ยวข้องกับการรวบรวมข้อมูล ทำความสะอาด ฝึกอบรมโมเดล ปรับแต่งโมเดล และการทดสอบต่อเนื่องที่เข้มข้น
แบบจำลองนี้ได้รับการฝึกฝนในคลังข้อมูลอันกว้างใหญ่เพื่อทำนายคำถัดไปในลำดับ ระยะนี้ช่วยให้โมเดลเรียนรู้ความเชื่อมโยงระหว่างคำที่หยิบยกรูปแบบทางไวยากรณ์ ความสัมพันธ์ที่สามารถแสดงถึงข้อเท็จจริงเกี่ยวกับโลก และความเชื่อมโยงที่ให้ความรู้สึกเหมือนเป็นการใช้เหตุผลเชิงตรรกะ การเชื่อมต่อเหล่านี้ยังทำให้เกิดอคติที่มีอยู่ในข้อมูลการฝึกอบรมอีกด้วย
หลังจากการฝึกอบรมล่วงหน้า โมเดลจะได้รับการปรับปรุงบนชุดข้อมูลที่แคบลง ซึ่งมักจะมีผู้ตรวจสอบที่เป็นมนุษย์ปฏิบัติตามหลักเกณฑ์
การปรับแต่งอย่างละเอียดถือเป็นขั้นตอนสำคัญในการสร้าง LLM โดยเกี่ยวข้องกับการฝึกอบรมโมเดลที่ได้รับการฝึกอบรมล่วงหน้าบนชุดข้อมูลหรืองานที่เฉพาะเจาะจงมากขึ้น ลองใช้ ChatGPT เป็นตัวอย่าง
หากคุณเคยเล่นกับโมเดล GPT คุณจะรู้ว่าการกระตุ้นนั้นน้อยกว่าการ "เขียนสิ่งนี้" และมีลักษณะคล้ายกันมากกว่า
- เกริ่นเรื่อง: กาลครั้งหนึ่ง
- ความต่อเนื่อง: มีพ่อมดชั่วร้ายอยู่บนยอดหอคอย
- ความต่อเนื่อง: มีพ่อมดชั่วร้ายอยู่บนยอดหอคอย
- Prompt : ทำไมไก่ถึงได้ร่วมวงดนตรี?
- ภาคต่อ : เพราะมีไม้ตีกลอง!
การจะเข้าสู่ ChatGPT จากจุดนั้นต้องใช้แรงงานค่าแรงต่ำจำนวนมาก คนเหล่านี้สร้างองค์กรขนาดใหญ่เพื่อให้ความสำคัญกับน้ำหนักของการตอบสนอง GPT และพฤติกรรมที่คาดหวัง ผู้ปฏิบัติงานเหล่านี้สร้างข้อความพร้อมท์/ข้อความต่อเนื่องมากมายที่มีลักษณะดังนี้:
- พร้อม : จบเรื่องนี้ : “กาลครั้งหนึ่ง..”
- ต่อ : แน่นอน! กาลครั้งหนึ่ง ณ ดินแดนอันไกลโพ้น มีหมู่บ้านเล็กๆ แห่งหนึ่งตั้งอยู่ระหว่างภูเขาสูงตระหง่านสองลูก
- ต่อ : แน่นอน! กาลครั้งหนึ่ง ณ ดินแดนอันไกลโพ้น มีหมู่บ้านเล็กๆ แห่งหนึ่งตั้งอยู่ระหว่างภูเขาสูงตระหง่านสองลูก
- Prompt : เล่าเรื่องตลกเกี่ยวกับไก่ให้ฉันฟังหน่อย
- ภาคต่อ : ทำไมไก่ถึงได้ร่วมวงดนตรี? เพราะว่ามันมีไม้ตีกลอง!
กระบวนการปรับแต่งอย่างละเอียดนี้มีความสำคัญด้วยเหตุผลหลายประการ:
- ความจำเพาะ: แม้ว่าการฝึกอบรมล่วงหน้าจะทำให้โมเดลมีความเข้าใจภาษาในวงกว้าง แต่การปรับแต่งอย่างละเอียดจะจำกัดความรู้และพฤติกรรมให้แคบลงเพื่อให้สอดคล้องกับงานหรือโดเมนที่เฉพาะเจาะจงมากขึ้น ตัวอย่างเช่น โมเดลที่ได้รับการปรับแต่งข้อมูลทางการแพทย์จะตอบคำถามทางการแพทย์ได้ดีขึ้น
- การควบคุม: การปรับแต่งอย่างละเอียดช่วยให้นักพัฒนาควบคุมเอาต์พุตของโมเดลได้มากขึ้น นักพัฒนาสามารถใช้ชุดข้อมูลที่รวบรวมไว้เพื่อเป็นแนวทางให้กับโมเดลเพื่อสร้างการตอบสนองที่ต้องการและหลีกเลี่ยงพฤติกรรมที่ไม่พึงประสงค์
- ความปลอดภัย: ช่วยลดผลลัพธ์ที่เป็นอันตรายหรือลำเอียง ด้วยการใช้แนวทางในระหว่างกระบวนการปรับแต่ง ผู้ตรวจสอบที่เป็นมนุษย์สามารถมั่นใจได้ว่าแบบจำลองจะไม่สร้างเนื้อหาที่ไม่เหมาะสม
- ประสิทธิภาพ: การปรับแต่งอย่างละเอียดสามารถปรับปรุงประสิทธิภาพของโมเดลในงานเฉพาะได้อย่างมาก ตัวอย่างเช่น โมเดลที่ได้รับการปรับแต่งอย่างละเอียดเพื่อการสนับสนุนลูกค้าจะดีกว่าโมเดลทั่วไปมาก
คุณสามารถบอกได้ว่า ChatGPT ได้รับการปรับแต่งอย่างละเอียดในบางด้าน
ตัวอย่างเช่น "การใช้เหตุผลเชิงตรรกะ" เป็นสิ่งที่ LLM มักจะประสบปัญหา โมเดลการให้เหตุผลเชิงตรรกะที่ดีที่สุดของ ChatGPT - GPT-4 - ได้รับการฝึกอบรมอย่างเข้มข้นเพื่อจดจำรูปแบบในตัวเลขอย่างชัดเจน
แทนที่จะเป็นสิ่งนี้:
- Prompt : 2+2 คืออะไร?
- กระบวนการ : บ่อยครั้งในหนังสือเรียนคณิตศาสตร์สำหรับเด็ก 2+2 = 4 ในบางครั้งอาจมีการอ้างอิงถึง "2+2=5" แต่โดยปกติแล้วจะมีบริบทเกี่ยวข้องกับ George Orwell หรือ Star Trek มากกว่าเมื่อเป็นเช่นนั้น หากเป็นเช่นนี้ น้ำหนักจะเข้าข้าง 2+2=5 มากกว่า แต่ไม่มีบริบทนั้น ดังนั้นในกรณีนี้ โทเค็นถัดไปน่าจะเป็น 4
- คำตอบ : 2+2=4
การฝึกอบรมทำหน้าที่ดังนี้:
- การฝึก: 2+2=4
- การฝึก: 4/2=2
- การฝึกอบรม: ครึ่งหนึ่งของ 4 คือ 2
- การฝึกอบรม: 2 จาก 2 คือสี่
…และอื่นๆ
ซึ่งหมายความว่าสำหรับโมเดลที่มี "ตรรกะ" มากกว่านั้น กระบวนการฝึกอบรมจะเข้มงวดมากขึ้นและมุ่งเน้นไปที่การทำให้แน่ใจว่าโมเดลนั้นเข้าใจและใช้หลักการเชิงตรรกะและคณิตศาสตร์อย่างถูกต้อง
แบบจำลองต้องเผชิญกับปัญหาทางคณิตศาสตร์ต่างๆ และแนวทางแก้ไข เพื่อให้แน่ใจว่าจะสามารถสรุปและประยุกต์ใช้หลักการเหล่านี้กับปัญหาใหม่ๆ ที่มองไม่เห็น
ความสำคัญของกระบวนการปรับแต่งนี้ โดยเฉพาะอย่างยิ่งสำหรับการใช้เหตุผลเชิงตรรกะ ไม่สามารถกล่าวเกินจริงได้ หากไม่มีแบบจำลองดังกล่าว แบบจำลองอาจให้คำตอบที่ไม่ถูกต้องหรือไร้สาระสำหรับคำถามเชิงตรรกะหรือคณิตศาสตร์ที่ตรงไปตรงมา
โมเดลรูปภาพกับโมเดลภาษา
แม้ว่าทั้งโมเดลรูปภาพและภาษาอาจใช้สถาปัตยกรรมที่คล้ายกัน เช่น หม้อแปลงไฟฟ้า แต่ข้อมูลที่ประมวลผลจะแตกต่างกันโดยพื้นฐาน:
โมเดลรูปภาพ
โมเดลเหล่านี้จัดการกับพิกเซลและมักจะทำงานในลักษณะลำดับชั้น โดยวิเคราะห์รูปแบบเล็กๆ (เช่น ขอบ) ก่อน จากนั้นจึงรวมเข้าด้วยกันเพื่อจดจำโครงสร้างที่ใหญ่ขึ้น (เช่น รูปร่าง) และต่อๆ ไปจนกว่าจะเข้าใจภาพทั้งหมด
โมเดลภาษา
โมเดลเหล่านี้ประมวลผลลำดับของคำหรืออักขระ พวกเขาจำเป็นต้องเข้าใจบริบท ไวยากรณ์ และความหมายเพื่อสร้างข้อความที่สอดคล้องกันและเกี่ยวข้องกับบริบท
อินเทอร์เฟซ AI เจนเนอเรชั่นที่โดดเด่นทำงานอย่างไร
Dall-E + กลางการเดินทาง
Dall-E เป็นอีกรุ่นหนึ่งของรุ่น GPT-3 ที่ปรับให้เหมาะกับการสร้างภาพ ได้รับการฝึกฝนเกี่ยวกับชุดข้อมูลคู่ข้อความและรูปภาพจำนวนมหาศาล Midjourney เป็นอีกหนึ่งซอฟต์แวร์สร้างภาพที่ใช้โมเดลที่เป็นกรรมสิทธิ์
- ข้อมูลที่ป้อน: คุณระบุคำอธิบายที่เป็นข้อความ เช่น "นกฟลามิงโกสองหัว"
- การประมวลผล: โมเดลเหล่านี้เข้ารหัสข้อความนี้เป็นชุดตัวเลข จากนั้นถอดรหัสเวกเตอร์เหล่านี้ ค้นหาความสัมพันธ์กับพิกเซล เพื่อสร้างภาพ โมเดลได้เรียนรู้ความสัมพันธ์ระหว่างคำอธิบายที่เป็นข้อความและการแสดงภาพจากข้อมูลการฝึกอบรม
- ผลลัพธ์: รูปภาพที่ตรงกันหรือเกี่ยวข้องกับคำอธิบายที่กำหนด
นิ้ว ลวดลาย ปัญหาต่างๆ
เหตุใดเครื่องมือเหล่านี้จึงไม่สามารถสร้างมือที่ดูปกติได้อย่างสม่ำเสมอ เครื่องมือเหล่านี้ทำงานโดยการดูพิกเซลที่อยู่ติดกัน
คุณสามารถดูวิธีการทำงานนี้เมื่อเปรียบเทียบรูปภาพที่สร้างก่อนหน้านี้หรือแบบดั้งเดิมกับรูปภาพล่าสุด: โมเดลก่อนหน้านี้ดูคลุมเครือมาก ในทางตรงกันข้าม โมเดลล่าสุดจะมีความคมชัดกว่ามาก
โมเดลเหล่านี้สร้างภาพโดยการทำนายพิกเซลถัดไปโดยพิจารณาจากพิกเซลที่สร้างขึ้นแล้ว กระบวนการนี้ถูกทำซ้ำหลายล้านครั้งเพื่อให้ได้ภาพที่สมบูรณ์
มือ โดยเฉพาะนิ้วมือนั้นซับซ้อนและมีรายละเอียดมากมายที่ต้องจับอย่างแม่นยำ
การวางตำแหน่ง ความยาว และการวางแนวของแต่ละนิ้วอาจแตกต่างกันอย่างมากในภาพต่างๆ
เมื่อสร้างภาพจากคำอธิบายที่เป็นข้อความ แบบจำลองจะต้องตั้งสมมติฐานหลายประการเกี่ยวกับท่าทางและโครงสร้างของมือ ซึ่งอาจนำไปสู่ความผิดปกติได้
ChatGPT
ChatGPT ใช้สถาปัตยกรรม GPT-3.5 ซึ่งเป็นโมเดลที่ใช้หม้อแปลงไฟฟ้าซึ่งออกแบบมาเพื่องานการประมวลผลภาษาธรรมชาติ
- ข้อมูลเข้า: ข้อความแจ้งหรือชุดข้อความเพื่อจำลองการสนทนา
- การประมวลผล: ChatGPT ใช้ความรู้มากมายจากข้อความทางอินเทอร์เน็ตที่หลากหลายเพื่อสร้างการตอบกลับ โดยพิจารณาบริบทที่ให้ไว้ในการสนทนาและพยายามสร้างคำตอบที่เกี่ยวข้องและสอดคล้องกันมากที่สุด
- เอาท์พุต: ข้อความตอบกลับที่ดำเนินการต่อหรือตอบการสนทนา
พิเศษ
จุดแข็งของ ChatGPT อยู่ที่ความสามารถในการจัดการหัวข้อต่างๆ และจำลองการสนทนาที่เหมือนมนุษย์ ทำให้เหมาะสำหรับแชทบอทและผู้ช่วยเสมือน
Bard + ประสบการณ์การสร้างการค้นหา (SGE)
แม้ว่ารายละเอียดเฉพาะอาจเป็นกรรมสิทธิ์ แต่ Bard ก็ใช้เทคนิค Transformer AI ซึ่งคล้ายกับโมเดลภาษาที่ล้ำสมัยอื่นๆ SGE ใช้โมเดลที่คล้ายกันแต่สานต่อในอัลกอริทึม ML อื่นๆ ที่ Google ใช้
SGE มีแนวโน้มที่จะสร้างเนื้อหาโดยใช้โมเดลการสร้างที่ใช้หม้อแปลงไฟฟ้า จากนั้นจึงแยกคำตอบออกจากหน้าการจัดอันดับในการค้นหาแบบคลุมเครือ (สิ่งนี้อาจไม่จริง เป็นเพียงการคาดเดาตามวิธีการเล่น โปรดอย่าฟ้องฉัน!)
- อินพุต: พรอมต์/คำสั่ง/ค้นหา
- การประมวลผล: Bard ประมวลผลอินพุตและทำงานในลักษณะเดียวกับ LLM อื่นๆ SGE ใช้สถาปัตยกรรมที่คล้ายกันแต่เพิ่มชั้นที่ค้นหาความรู้ภายใน (ได้มาจากข้อมูลการฝึกอบรม) เพื่อสร้างการตอบสนองที่เหมาะสม โดยพิจารณาโครงสร้าง บริบท และความตั้งใจในการสร้างเนื้อหาที่เกี่ยวข้อง
- ผลลัพธ์: เนื้อหาที่สร้างขึ้นซึ่งอาจเป็นเรื่องราว คำตอบ หรือข้อความประเภทอื่นๆ
การประยุกต์ใช้ generative AI (และข้อโต้แย้ง)
ศิลปะและการออกแบบ
Generative AI สามารถสร้างงานศิลปะ เพลง และแม้แต่การออกแบบผลิตภัณฑ์ได้แล้ว สิ่งนี้ได้เปิดช่องทางใหม่สำหรับความคิดสร้างสรรค์และนวัตกรรม
การโต้เถียง
การเพิ่มขึ้นของ AI ในงานศิลปะทำให้เกิดข้อถกเถียงเกี่ยวกับการตกงานในสาขาสร้างสรรค์
นอกจากนี้ ยังมีข้อกังวลเกี่ยวกับ:
- การละเมิดด้านแรงงาน โดยเฉพาะอย่างยิ่งเมื่อมีการใช้เนื้อหาที่สร้างโดย AI โดยไม่มีการระบุแหล่งที่มาหรือการชดเชยที่เหมาะสม
- ผู้บริหารข่มขู่นักเขียนด้วยการแทนที่พวกเขาด้วย AI เป็นปัญหาหนึ่งที่กระตุ้นให้นักเขียนหยุดงานประท้วง
การประมวลผลภาษาธรรมชาติ (NLP)
ปัจจุบันโมเดล AI ถูกนำมาใช้กันอย่างแพร่หลายสำหรับแชทบอท การแปลภาษา และงาน NLP อื่นๆ
นอกเหนือจากความฝันของปัญญาประดิษฐ์ทั่วไป (AGI) นี่คือการใช้งานที่ดีที่สุดสำหรับ LLM เนื่องจากใกล้เคียงกับโมเดล NLP "ทั่วไป"
การโต้เถียง
ผู้ใช้หลายคนพบว่าแชทบอทไม่มีตัวตนและบางครั้งก็น่ารำคาญ
ยิ่งไปกว่านั้น แม้ว่า AI จะมีความก้าวหน้าอย่างมากในการแปลภาษา แต่ก็มักจะขาดความแตกต่างและความเข้าใจทางวัฒนธรรมที่นักแปลมนุษย์นำมา ซึ่งนำไปสู่การแปลที่น่าประทับใจและมีข้อบกพร่อง
การค้นพบยาและยา
AI สามารถวิเคราะห์ข้อมูลทางการแพทย์จำนวนมหาศาลได้อย่างรวดเร็ว และสร้างสารประกอบยาที่มีศักยภาพ ซึ่งช่วยเร่งกระบวนการค้นพบยาให้เร็วขึ้น แพทย์จำนวนมากใช้ LLM ในการเขียนบันทึกและการสื่อสารกับคนไข้อยู่แล้ว
การโต้เถียง
การใช้ LLM เพื่อวัตถุประสงค์ทางการแพทย์อาจเป็นปัญหาได้ การแพทย์ต้องการความแม่นยำ และข้อผิดพลาดหรือการกำกับดูแลโดย AI อาจส่งผลร้ายแรง
การแพทย์ก็มีอคติอยู่แล้ว มีแต่จะได้รับประโยชน์มากขึ้นจากการใช้ LLM เท่านั้น นอกจากนี้ยังมีประเด็นที่คล้ายกัน ดังที่อธิบายไว้ด้านล่างนี้ เกี่ยวกับความเป็นส่วนตัว ประสิทธิภาพ และจริยธรรม
การเล่นเกม
ผู้ที่ชื่นชอบ AI จำนวนมากรู้สึกตื่นเต้นกับการใช้ AI ในการเล่นเกม พวกเขากล่าวว่า AI สามารถสร้างสภาพแวดล้อมการเล่นเกมที่สมจริง ตัวละคร และแม้กระทั่งเนื้อเรื่องในเกมทั้งหมด ซึ่งช่วยยกระดับประสบการณ์การเล่นเกม สามารถปรับปรุงบทสนทนาของ NPC ได้โดยใช้เครื่องมือเหล่านี้
การโต้เถียง
มีการถกเถียงกันเกี่ยวกับความตั้งใจในการออกแบบเกม
แม้ว่า AI จะสามารถสร้างเนื้อหาจำนวนมหาศาลได้ แต่บางคนแย้งว่า AI ยังขาดการออกแบบที่ตั้งใจและการทำงานร่วมกันในการเล่าเรื่องที่นักออกแบบที่เป็นมนุษย์นำมาใช้
Watchdogs 2 มี NPC แบบเป็นโปรแกรม ซึ่งช่วยเสริมการเล่าเรื่องของเกมโดยรวมได้เพียงเล็กน้อย
การตลาดและการโฆษณา
AI สามารถวิเคราะห์พฤติกรรมผู้บริโภคและสร้างโฆษณาและเนื้อหาส่งเสริมการขายส่วนบุคคล ทำให้แคมเปญการตลาดมีประสิทธิภาพมากขึ้น
LLM มีบริบทจากงานเขียนของผู้อื่น ทำให้มีประโยชน์สำหรับการสร้างเรื่องราวของผู้ใช้หรือแนวคิดเชิงโปรแกรมที่เหมาะสมยิ่งขึ้น แทนที่จะแนะนำทีวีให้กับผู้ที่เพิ่งซื้อทีวี LLM สามารถแนะนำอุปกรณ์เสริมที่บางคนอาจต้องการแทนได้
การโต้เถียง
การใช้ AI ในด้านการตลาดทำให้เกิดข้อกังวลเรื่องความเป็นส่วนตัว There's also a debate about the ethical implications of using AI to influence consumer behavior.
Dig deeper: How to scale the use of large language models in marketing
Continuing issues with LLMS
Contextual understanding and comprehension of human speech
- Limitation: AI models, including GPT, often struggle with nuanced human interactions, such as detecting sarcasm, humor, or lies.
- Example: In stories where a character is lying to other characters, the AI might not always grasp the underlying deceit and might interpret statements at face value.
Pattern matching
- Limitation: AI models, especially those like GPT, are fundamentally pattern matchers. They excel at recognizing and generating content based on patterns they've seen in their training data. However, their performance can degrade when faced with novel situations or deviations from established patterns.
- Example: If a new slang term or cultural reference emerges after the model's last training update, it might not recognize or understand it.
Lack of common sense understanding
- Limitation: While AI models can store vast amounts of information, they often lack a "common sense" understanding of the world, leading to outputs that might be technically correct but contextually nonsensical.
Potential to reinforce biases
- Ethical consideration: AI models learn from data, and if that data contains biases, the model will likely reproduce and even amplify those biases. This can lead to outputs that are sexist, racist, or otherwise prejudiced.
Challenges in generating unique ideas
- Limitation: AI models generate content based on patterns they've seen. While they can combine these patterns in novel ways, they don't "invent" like humans do. Their "creativity" is a recombination of existing ideas.
Data Privacy, Intellectual Property, and Quality Control Issues:
- Ethical consideration : Using AI models in applications that handle sensitive data raises concerns about data privacy. When AI generates content, questions arise about who owns the intellectual property rights. Ensuring the quality and accuracy of AI-generated content is also a significant challenge.
Bad code
- AI models might generate syntactically correct code when used for coding tasks but functionally flawed or insecure. I have had to correct the code people have added to sites they generated using LLMs. It looked right, but was not. Even when it does work, LLMs have out-of-date expectations for code, using functions like “document.write” that are no longer considered best practice.
Hot takes from an MLOps engineer and technical SEO
This section covers some hot takes I have about LLMs and generative AI. Feel free to fight with me.
Prompt engineering isn't real (for generative text interfaces)
Generative models, especially large language models (LLMs) like GPT-3 and its successors, have been touted for their ability to generate coherent and contextually relevant text based on prompts.
Because of this, and since these models have become the new “gold rush," people have started to monetize “prompt engineering” as a skill. This can be either $1,400 courses or prompt engineering jobs.
However, there are some critical considerations:
LLMs change rapidly
As technology evolves and new model versions are released, how they respond to prompts can change. What worked for GPT-3 might not work the same way for GPT-4 or even a newer version of GPT-3.
This constant evolution means prompt engineering can become a moving target, making it challenging to maintain consistency. Prompts that work in January may not work in March.
Uncontrollable outcomes
While you can guide LLMs with prompts, there's no guarantee they'll always produce the desired output. For instance, asking an LLM to generate a 500-word essay might result in outputs of varying lengths because LLMs don't know what numbers are.
Similarly, while you can ask for factual information, the model might produce inaccuracies because it cannot tell the difference between accurate and inaccurate information by itself.
Using LLMs in non-language-based applications is a bad idea
LLMs are primarily designed for language tasks. While they can be adapted for other purposes, there are inherent limitations:
Struggle with novel ideas
LLMs are trained on existing data, which means they're essentially regurgitating and recombining what they've seen before. They don't "invent" in the truest sense of the word.
Tasks that require genuine innovation or out-of-the-box thinking should not use LLMs.
You can see an issue with this when it comes to people using GPT models for news content – if something novel comes along, it's hard for LLMs to deal with it.

For example, a site that seems to be generating content with LLMs published a possibly libelous article about Megan Crosby. Crosby was caught elbowing opponents in real life.
Without that context, the LLM created a completely different, evidence-free story about a “controversial comment.”
Text-focused
At their core, LLMs are designed for text. While they can be adapted for tasks like image generation or music composition, they might not be as proficient as models specifically designed for those tasks.
LLMs don't know what the truth is
They generate outputs based on patterns encountered in their training data. This means they can't verify facts or discern true and false information.
If they've been exposed to misinformation or biased data during training, or they don't have context for something, they might propagate those inaccuracies in their outputs.
This is especially problematic in applications like news generation or academic research, where accuracy and truth are paramount.
Think about it like this: if an LLM has never come across the name “Jimmy Scrambles” before but knows it's a name, prompts to write about it will only come up with related vectors.
Designers are always better than AI-generated Art
AI has made significant strides in art, from generating paintings to composing music. However, there's a fundamental difference between human-made art and AI-generated art:
Intent, feeling, vibe
Art is not just about the final product but the intent and emotion behind it.
A human artist brings their experiences, emotions, and perspectives to their work, giving it depth and nuance that's challenging for AI to replicate.
A “bad” piece of art from a person has more depth than a beautiful piece of art from a prompt.
ความคิดเห็นที่แสดงในบทความนี้เป็นความคิดเห็นของผู้เขียนรับเชิญ และไม่จำเป็นต้องเป็น Search Engine Land ผู้เขียนเจ้าหน้าที่มีอยู่ที่นี่
